BTS INFRASTRUCTURE FABRICATION AND DEPLOYMENT
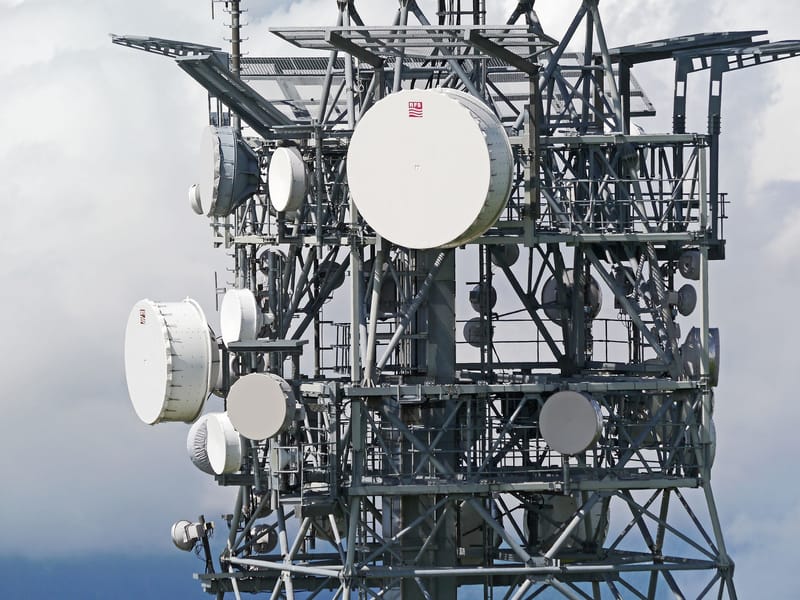

INTRODUCTION TO CELL TOWER
In the early period invention of GSM, people wondered how cell phone users were able to connect to the world, despite being miles away from each other. The answer lies in cell towers, the silent architects of our modern, connected lives. These structures, scattered across the landscape, enable our mobile devices to communicate with each other, providing us with the seamless connectivity we’ve come to rely on.
WHAT IS CELL TOWER THEN?
A cell tower is a steel or iron structure (usually galvanized to avoid rusting and other degrading factors acting on it) equipped with antennas, transmitters, and receivers that facilitate wireless communication. Cell towers transmit and receive radio signals to and from mobile devices, providing both geographical coverage and the capacity to handle thousands of user voice and data connections simultaneously. It’s a critical component in a cellular network, which allows mobile devices like cell phones and tablets to connect to the internet and make calls. Cell towers are also known as cellular towers, cell phone towers, antenna towers, communication towers, mobile towers, telecom towers, telephone towers, wireless communication towers, and 5G towers.

So, what is a 5G Tower: These are large structures that support multiple sets of equipment from various wireless carriers. They're designed to accommodate antennas, Remote Radio Heads (RRH), and other vital telecom gears. Small Cells: Much more compact, small cells typically fit within a volume of 25 cubic feet. cell tower comprises several essential components that enable it to provide wireless communication to mobile phones and tablets. Some of the key components include:
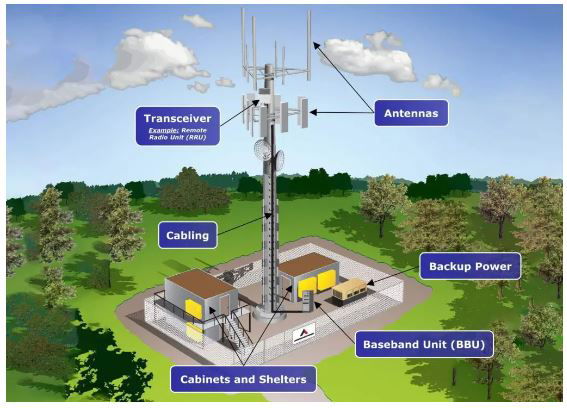 Adapted From: American Tower
Adapted From: American Tower
- Antennas: These send and receive radio frequency (RF) signals from the tower to a cell phone or vice versa. Cell towers usually have multiple antennas, each set to a different frequency that are often placed at varying heights on the structure
- Transceiver: This is the radio unit that helps in transmitting and receiving signals. In modern cell phone towers, using 4G/LTE and 5G, a Remote Radio Unit (RRU), also sometimes referred to as a Remote Radio Head (RRH), is placed on the top of the structure
- Baseband Unit (BBU): This handles the communication protocols and is responsible for setting up, maintaining, and terminating calls or data sessions. It is often deployed at the bottom of the tower
- Primary Power: Typically a direct electrical grid connection, which is used to power transmission equipment, cooling systems, lighting, and other operational needs
- Backup Power: In case of a power outage, cell towers use diesel generators and/or battery banks as an emergency power source to keep operating
- Cabling: Coaxial and/or fiber lines are used to transmit the signal received from the antenna to the base station or vice versa
- Cabinets and Shelters: Buildings at the base of cell phone towers used to house communications, radio, and network equipment
BTS INFRASTRUCTURE FABRICATION AND DEPLOYMENT AS A SERVICE
At X-PLUS TELECOMS & TOWERS, we have the expertise for site deployments, both, a comprehensive and integrated approach to support the telecom infrastructure that was developed over the years. We provide infrastructures that empower the future of connectivity supporting telecommunications operators by offering a suite of 5G tower infrastructure solutions for leasing that can be tailored to cater to the demands and requirements specifically of the African market. In recent years we had the opportunity to complete more than 1,000 BTS sites with our partners in Nigeria, and other West African states. In most cases, we were required to fabricate, galvanize, and perform all the civil work required in actualizing the project implementation

We fabricate, galvanize, and deploy the various types of Telecommunication Towers.
- Lattice Towers: They are freestanding and segmentally designed with rectangular or triangular base steel lattices. This type of tower construction can be useful in situations that require modifications such as mounting a large number of panels or dish antennas. They can be used as electricity transmission towers, radio towers, or as observation towers. The Eiffel Tower is a famous example of a lattice tower.
- Guyed Towers: They are lightweight to heavyweight towers often seen as slender steel structures. Commonly seen in the tower industry, guyed towers are designed to provide maximum strength, efficiency, and versatility with easy installation. They are supported by one or more levels of braided or stranded steel guy cables that anchor to the ground.
- Monopole Towers: These types of towers are required when the space for installation is limited.
- Camouflage Towers: They are often seen in the form of artificial pine trees, palm trees, clock towers, and even in the form of artificial cacti.
- Self-Support Towers: Self-support towers offer the most possibilities compared to other types of telecom towers and are considered appropriate for nearly all wireless communication applications. We offer them in 3-legged triangular and 4-legged square lattice-type structures, their braces can accommodate the heaviest of loads and the strongest of winds. Their design is ideal for installations where space requirements may be limited and often inexpensive to purchase, transport, and install.


